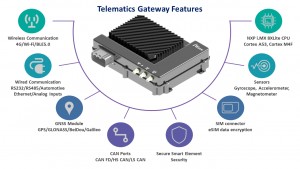
As vehicles evolve into sophisticated, connected platforms, the need for robust telematics solutions becomes increasingly critical for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These solutions must ensure seamless communication both within the vehicle’s internal networks and with external cloud services. A pivotal component in achieving this connectivity is the Telematics Gateway Module. This device serves as the central hub, facilitating real-time data computation, analysis, and intuitive user interaction for controlling diverse vehicle operations.
The telematics gateway module engineered by iWave offers a versatile and adaptable computing platform specifically designed for the automotive industry. It empowers automakers with the capability to manage data exchange between numerous Electronic Control Units (ECUs) and remote servers efficiently and securely. Prioritizing data integrity and security, this module establishes a fortified execution environment, effectively preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive vehicle data.
Integrating a broad spectrum of interfaces, the telematics gateway excels at gathering vital data from various vehicle subsystems. This rich data collection capability empowers users with actionable insights, driving improvements in vehicle efficiency, performance monitoring, and advanced service delivery.
Key Features of Telematics Gateway Modules
- Advanced Wireless Communication Capabilities:
Modern telematics gateway modules are equipped with cutting-edge wireless technologies to ensure reliable and high-speed data transmission. This includes 4G/LTE Cat 4/Cat M1, essential for rapid Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) applications within the automotive context. Furthermore, options like Wi-Fi 802.11a/b/g/n/ac, with potential upgrades to 802.11ax, BLE 5.0, and Ultra-Wideband (UWB) wireless transceivers, provide versatile pathways for data transfer between the vehicle and cloud platforms. These wireless capabilities are foundational for over-the-air (OTA) updates, real-time diagnostics, and connected infotainment services.
- Comprehensive Wired Interface Options:
Beyond wireless, robust wired interfaces are crucial for telematics gateways to interface with the complex in-vehicle network. Interfaces such as RS232, RS485, Automotive Ethernet, and Analog Inputs provide dependable and high-throughput communication protocols. These are indispensable for supporting advanced automotive technologies including Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS), autonomous driving functionalities, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, and high-bandwidth data logging requirements for vehicle performance analysis and development. Automotive Ethernet, in particular, is becoming increasingly important for handling the large data streams generated by modern vehicle sensors and systems.
- High-Performance Processing with i.MX 8 DXL CPU:
At the core of many advanced telematics gateway modules is a powerful processor like the i.MX 8 DXL, featuring a 64-bit ARMv8 architecture. This System on Chip (SoC) typically integrates dynamic power scaling with ARM Cortex A35 and ARM Cortex M4 processors, alongside substantial internal memory like 2GiB. This processing power is essential for demanding tasks such as sophisticated fleet management algorithms, complex vehicle configurations, remote diagnostics, and advanced edge computing applications directly within the vehicle. The multi-core architecture allows for efficient handling of concurrent tasks, ensuring responsiveness and reliability.
- Precise and Uninterrupted Vehicle Location Tracking:
Accurate and reliable location data is fundamental for telematics applications. High-precision Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) modules, supporting constellations like GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo, are integral to telematics gateway modules. These modules ensure uninterrupted, high-accuracy vehicle location tracking, critical for navigation, geofencing, asset tracking, and various location-based services. Advanced GNSS solutions often incorporate dead reckoning capabilities to maintain location accuracy even in areas with poor satellite signal reception, such as urban canyons or tunnels.
- Real-time Vehicle Monitoring via CAN Interfaces:
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is the backbone of in-vehicle communication. Telematics gateway modules are equipped with High-speed CAN-FD transceivers, often supporting up to 5 CAN-FD channels with data speeds reaching 5Mbps. This high-bandwidth capability is essential for real-time vehicle monitoring. Support for industry-standard protocol stacks like ISO 15765-4 CAN, SAE J1939, ISO 11898, CANopen, and CiA 447 ensures compatibility with a wide range of vehicle systems and equipment. This makes telematics gateways suitable for diverse applications from heavy-duty trucks and off-road vehicles to emergency service fleets and complex mobility infrastructures, enabling comprehensive vehicle diagnostics and performance data acquisition.
- Smart Sensors for Continuous Environmental and Motion Monitoring:
To provide a holistic view of vehicle operation and environment, telematics gateways often integrate smart sensors. These typically include 3-axis gyroscopes, accelerometers, and magnetometers. These sensors enable real-time motion monitoring, advanced driver behavior analysis (detecting harsh braking, acceleration, or cornering), and facilitate auto-calibration of other vehicle systems. Data from these sensors can be used to optimize driving patterns, improve vehicle safety, and trigger alerts based on detected motion events or environmental changes.
- Secure and Flexible SIM Connectivity:
For cellular communication, telematics gateways incorporate SIM connector technology, often with a focus on enhanced security. High-security eSIM options with robust data encryption are increasingly common. Support for multiple IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and multiple Profile UICC (Universal Integrated Circuit Card) SIM technologies allows for flexible network management and remote profile/applet management. This is crucial for global deployments, enabling seamless switching between mobile network operators and enhancing security against unauthorized network access.
- Multi-Dimensional Security Mechanisms:
Security is paramount in connected vehicles. Telematics gateway modules employ multi-layered security mechanisms to protect against cyber threats. Incorporating a Hardware Secure Element (HSE), such as the NCJ38A, provides a strong foundation for security. This restricts unauthorized application installations, ensuring that only trusted applications and devices can access the gateway. Features like secure boot, secure storage, and hardware-based cryptographic acceleration further enhance the security posture of the telematics gateway, safeguarding sensitive vehicle data and control systems.
Selecting the Right Telematics Gateway Module
Choosing the optimal telematics gateway module is a critical decision that depends on a variety of factors tailored to specific application needs. Key considerations include the nature of the client base, operational geographical regions, typical distances covered, and the specific types of vehicles being deployed.
-
Extensive and Adaptable Connectivity Options: In the landscape of connected mobility, reliable connectivity is paramount. The ideal telematics gateway module must offer adaptable connectivity solutions, capable of scaling communication standards based on the vehicle’s specific infrastructure requirements. Depending on the intended application, the gateway should support a range of wireless communication technologies, including Wi-Fi, BLE, LTE, and potentially emerging standards like DSRC (Dedicated Short-Range Communications) or 5G as needed. This adaptability ensures future-proofing and broadens the range of deployable applications.
-
Versatility in Data Collection Interfaces: The automotive industry is characterized by a vast diversity of vehicle manufacturers, models, and configurations. To effectively collect data across this heterogeneous environment, a telematics gateway module needs a modular architecture that supports a wide array of interfaces. This includes CAN, Ethernet, J1939 (for heavy-duty vehicles), RS232, RS485, and potentially other specialized interfaces. This interface versatility ensures compatibility with different vehicle ECUs and sensor systems, maximizing the scope of data that can be collected for analysis and application use.
-
Software Flexibility for Diverse Fleet and Asset Management: Managing diverse fleets and assets efficiently requires a telematics gateway module with scalable and adaptable software capabilities. The software on the device must facilitate simultaneous tracking of both vehicles and associated assets. Crucially, the supported software stacks should ensure interoperability across different vehicle types and mobility infrastructures. This interoperability is key to reducing development time for customized applications, allowing for quicker deployment and adaptation to specific fleet management needs. Open platforms and well-documented APIs are highly desirable for enabling seamless software integration and customization.
Value Added Services from iWave
-
Global Certifications for Market Access: To ensure compliance and facilitate global deployment, the iWave telematics gateway module is pre-certified with essential global standards including FCC (United States), CE (Europe), and ISED (Canada). Furthermore, iWave extends support for obtaining country-specific certifications such as KOMINFO (Indonesia) and E-Mark (Europe, for automotive components). These certifications significantly streamline the regulatory approval process for OEMs, accelerating time-to-market in various regions.
-
Accelerated Pre-Programming Cycle: iWave provides user-friendly Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) designed to simplify the development process. These APIs eliminate the complexities associated with intricate embedded scripting and proprietary device management tools. This ease of use drastically shortens the pre-programming cycle, allowing developers to quickly implement and customize telematics applications, reducing development costs and time.
-
Customization Services for Tailored Solutions: Recognizing the diverse needs of automotive applications, iWave offers comprehensive customization services for their telematics gateway module. These services encompass hardware feature modifications, enclosure design adaptations to suit specific environmental conditions, and branding options for OEMs seeking to integrate the gateway seamlessly into their product lines. This customization capability ensures that the telematics solution can be precisely tailored to meet unique project requirements.
-
Enhanced Security Feature Add-ons: Addressing the critical concern of cybersecurity in connected vehicles, iWave provides an optional security suite to augment the telematics gateway module’s security posture. This suite includes features like Secure Boot to prevent unauthorized firmware loading, Secure Storage for protecting sensitive data at rest, and Wi-Fi Security enhancements to safeguard wireless communication channels. These add-on security features provide an extra layer of protection against potential vulnerabilities and cyberattacks.
Telematics Gateway Module Use Cases Across Industries
-
Predictive Maintenance in Electric Vehicles (EVs): For electric vehicle drivers, understanding battery health, charge levels, and locating nearby charging stations are crucial for efficient trip planning and vehicle management. Telematics gateway modules, with their extensive onboard features and versatile wired and wireless interfaces, are instrumental in providing the valuable data streams needed to refine EV algorithms for predictive maintenance, range estimation, and battery optimization. Real-time monitoring of battery parameters, motor performance, and charging cycles enables proactive maintenance alerts and enhances overall EV reliability and driver confidence.
-
Precision Control and Tracking of Farm Equipment: Manufacturers of modern farm equipment are focused on enhancing farmer productivity through secure data sharing and operational insights. Telematics gateway modules installed in tractors, harvesters, and other agricultural vehicles enable precise tracking of equipment movement, location within fields, driver status, fuel consumption, and operational hours. This data empowers farmers to optimize equipment utilization, improve operational efficiency, and manage their agricultural assets more effectively, leading to increased yields and reduced operational costs.
-
Optimized Fleet Management for Enhanced Efficiency: In fleet management, operational failures like vehicle breakdowns or recalls can lead to significant financial losses and service disruptions. Telematics gateway modules mitigate these risks by providing built-in interfaces like CAN, RS232, and RS485 to collect and securely transmit critical fleet information to operators. Real-time data on vehicle health, location, driver behavior, and fuel efficiency enhances fleet productivity, reduces downtime, enables proactive maintenance scheduling, and ultimately minimizes costly failures and operational inefficiencies.
-
Robust Performance for Heavy-Duty and Off-Road Vehicles: Heavy-duty vehicles like forklifts, cranes, and construction trucks often operate in extreme conditions and for extended hours, making them susceptible to frequent breakdowns and demanding rigorous maintenance schedules. Telematics gateway modules with integrated J1939 protocol support are ideally suited for these applications. They can retrieve comprehensive diagnostic information and real-time operational data directly from the vehicle’s ECUs. This capability ensures maximized vehicle uptime, facilitates predictive maintenance strategies, and optimizes the operational lifespan of heavy-duty and off-road equipment, reducing operational costs and improving productivity in demanding environments.
For detailed specifications or further inquiries, please contact [email protected]
Further Reading
| Embedded Telematics: Unlocked | Security Suite for the Automotive Industry | OBD II for IoT Fleet Management |
|---|